Periodic Table

Podcast
Understanding the Periodic Table
The periodic table is a fundamental tool in science that organizes the chemical elements. This blog post will explain how the periodic table works.
The periodic table is a visual representation of the periodic law. This law states that when elements are organized by their atomic numbers, you can see patterns in their properties. The periodic table helps us understand these patterns and how elements relate to one another.
How is the Periodic Table Organized?
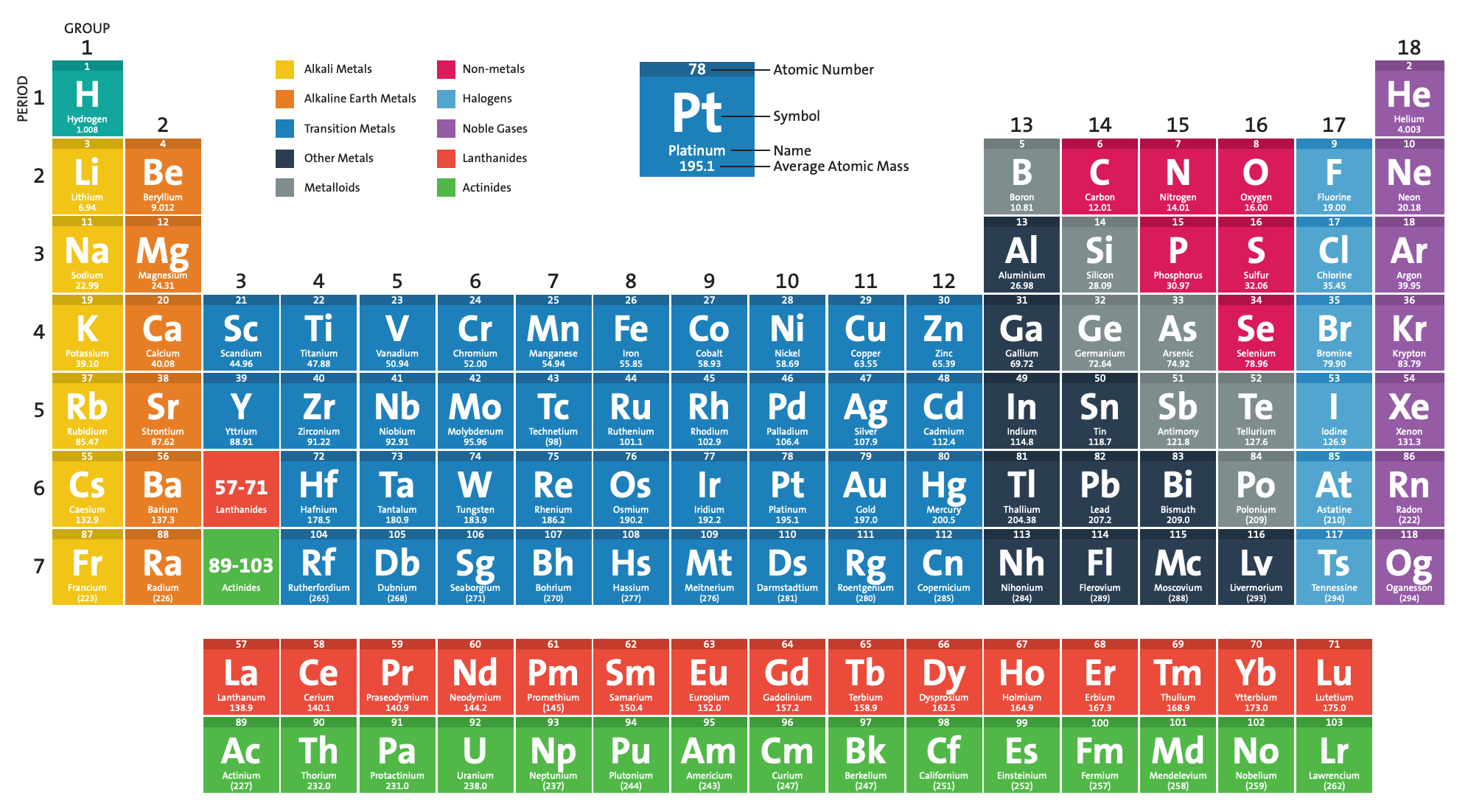
- Atomic Number: The periodic table organizes elements based on their atomic number. This number represents how many protons are in an element's nucleus. For example, hydrogen (H) has an atomic number of 1 because it has one proton, while helium (He) has an atomic number of 2.
- Periods and Groups: Elements are arranged in rows called periods, and columns called groups. Elements in the same group often share similar chemical behavior.
- Blocks: The periodic table is also divided into four blocks (s, p, d, f) based on the arrangement of electrons in their outermost shell.
Here is an example of a periodic table:
Why Is Electron Configuration Important?
- Each element has a unique electron configuration, which describes how the electrons are arranged in different energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
- The arrangement of electrons determines an element's chemical properties. Elements in the same group have similar electron configurations in their outermost shell, explaining their similar chemical behavior.
Let's Summarize the Key Points:
- The periodic table organizes the elements based on their atomic number.
- It is structured into periods, groups, and blocks to reveal repeating patterns in element properties.
- The periodic table is based on the periodic law, which states that properties of elements recur periodically when organized by atomic number.
- Electron configuration plays a crucial role in understanding why elements in the same group share similar chemical behavior.
The periodic table is a powerful tool. It allows scientists to predict the properties of elements and how they will react with one another.